2020 highlighted business leaders’ lack of preparedness in preventing future supply chain … [+]
GETTY
Supply chain disruptions brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic have exposed businesses to new vulnerabilities and their collective impact on the world economy. As a result, most companies either spent FY2020 fighting fires in response to increased online orders or taking a financial hit to deploy new services and business models to help retain and acquire new customers.
In both instances, 2020 shook business leaders awake to the importance of their supply chain, specifically their lack of visibility into the systems and processes that could hasten logistics and prevent fulfillment issues as (or before) they occur.
It’s important to note that the supply chain issues experienced last year were not solely caused by consumer behavior changes during lockdown. In fact, 40 percent of executives believe their exposure to supply chain risks have increased over the past three years. What’s more surprising is that even though 92 percent of executives agree supply chain visibility is important to success, only 27 percent have figured out a way to achieve it. This stark difference between intent and application leaves a huge opportunity for category disruption, innovation, and of course, investment.
Only 27 percent of executives have figured out a way to achieve adequate supply chain visibility.
GETTY
Market Trends & Predictions
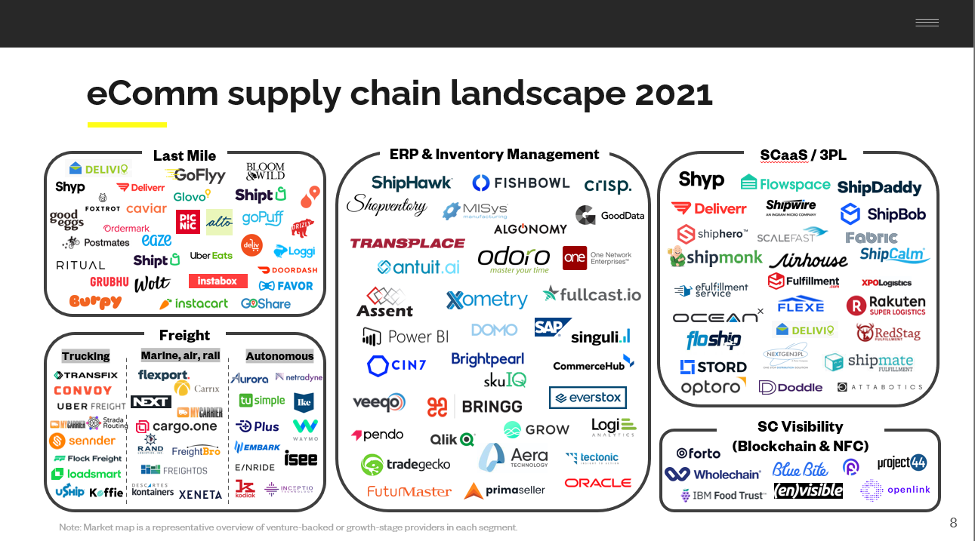
According to Pitchbook’s most recent Supply Chain Technology report, venture investment in supply chain tech startups totaled $7.7 billion across 186 deals in Q1 2021, up 90.6% QoQ and 355.1% YoY compared to 2020.
Additionally, Pitchbook estimates that the global supply chain technology market is expected to top $6 trillion by 2025 across the verticals of freight, warehousing & fulfillment, enterprise supply chain management (SCM) and last-mile delivery.
This impressive traction begs the question—what’s driving growth in supply chain tech and where is innovation happening?
1) Evolving consumer expectations for free and fast delivery will hasten innovations in last-mile logistics.
Before COVID, consumers were already becoming accustomed to the concept of “free and fast” delivery through their familiarity with services like Amazon Prime. Today, these expectations have accelerated with next-day, same-day and even same hour options appearing across industries.
Additionally, recent research suggests that 96 percent of today’s consumers consider “fast delivery” to mean “same-day” delivery, yet only 51 percent of retailers offer this option. Given these expectations, it will be critical for businesses to shorten the distance between their warehouse(s) and their customers to enable faster shipping times.
However, this is easier said than done. Right now, last mile delivery (the act of transporting goods from a local distribution center to a customer’s front door) comprises a substantial portion of overall logistics costs at 53 percent. Moving forward, it will be mission critical for businesses to get that number down to improve margins before they can improve the last mile.
Startups like Unoecom (Delivio) are attempting to help businesses do just that by turning people’s homes into “micro fulfillment centers” to reduce last mile delivery costs. Under this gig-inspired business model, Delivio plans to monetize unused space in people’s homes and pay workers for their storage (and fulfillment) services, if they also own a car.
Right now, last mile delivery comprises 53 percent of overall logistics costs.
GETTY
2) Decentralized fulfillment will become the new norm for all companies, not just those big enough to own their own supply chains
In the past, centralized distribution was preferred to decentralized models because it allows for superior bargaining power with suppliers and lower storage costs (i.e. it’s cheaper for suppliers to bulk-ship product to one location instead of a handful of smaller warehouses across the country).
However, today’s consumers want their items quickly, which means the increased shipping times from a single, central warehouse to a customer’s front door are no longer worth the cost savings. In fact, the cost of customer churn due to a slow delivery experience may now outweigh the savings gained from centralized models.
For all these reasons, having a decentralized warehouse network is now looked at as the leading fulfillment solution. That said, small eComm retailers have historically lacked the capital to own and operate multiple warehouses, making it hard for them to execute decentralized business models… until recently.
3) New innovations in “Supply Chain as a Service” (SCaaS) will give SMEs the means to scale affordably.
Outsourced logistics were rare before the 1990s. Now, businesses everywhere are realizing that handling their own warehousing and fulfillment services isn’t the most productive or cost-effective. While this is particularly true for SMEs, outsourced logistics are now gaining popularity with companies of all sizes.
In 2021, there will be increased enthusiasm for third party logistics (3PL) solutions that help companies turn fixed expenditures into variable costs without large capital expenses or ongoing maintenance fees. Particularly, 2PL and 3PL providers have been seeing increased demand from D2C eComm retailers due to their ability to help companies scale without all the upfront investment.
Modern 2PL startups like Transfix are helping companies revolutionize their fleet through advanced transportation management systems (TMS), and new 3PL companies like Flexe and Stord are providing on-demand, scalable warehousing solutions and cloud-based SCM software for growing businesses.
Outsourced logistics are now gaining popularity with companies of all sizes.
GETTY
4) Increased demand for ethical sourcing and sustainability will pave the way for innovations in SCM.
Before recent innovations in SCM technology, the only companies that invested in supply chain visibility were those most prone to counterfeiting (i.e., luxury fashion and cosmetic brands). However, as investors set new standards for ESG compliance and consumers demand higher levels of social and ethical consciousness by the companies they support, it is now more critical than ever for businesses to double down on their supply chain transparency efforts.
Adding to this urgency are new laws being proposed by the FDA to enforce greater “farm-to-table” traceability of food products. FSMA Rule 204 is one such proposal that signals a major shift toward what the industry is calling a “New Era of Smarter Food Safety”. If Rule 204 is passed—which at the moment, looks like it will be— companies will have exactly two years to begin complying with a strict, new set of standards that mandate increased record-keeping and the enhanced tracking and tracing of food products across the entire food system.
While Rule 204 would invite positive change for the industry, it’s worth noting that ensuring supply chain visibility is currently the single most challenging area for supply chain leaders to tackle, meaning businesses everywhere will be looking for solutions to get ahead of it. This is why startups like Wholechain and ProQure are so exciting, and why it’s important for investors to be thinking about not only how companies can enable trust, coordination, and transparency in their supply chains, but also how they can communicate that transparency to consumers. Blockchain technology is one exciting advancement that is predicted to change the dynamic in this space.
Looking Ahead
Coming out of the rocky foundation left by the pandemic, it will be more important than ever for consumer-focused VCs to evaluate companies’ supply chain strategy before considering an investment, and to be on the lookout for startups that proactively solve supply chain issues that their portcos may experience in the future.